What is Graphene ?!
A lot of people hear about Graphene but don’t know accurately about it and ask this question What is Graphene ?! and what it uses and features ?! and how can change human future ?!
Graphene Story:
Graphene starts as a dream and first studied theoretically in the 1940s. At the time, scientists thought it was physically impossible for a two-dimensional material to exist, so they did not pursue isolating graphene. Decades later, interest picked up and researchers began dreaming up techniques to peel apart graphite. They tried wedging molecules between layers of graphene and scraping and rubbing graphite, but they never got to a single layer. Eventually, they were able to isolate graphene on top of other materials, but not on its own.
In 2002, University of Manchester researcher Andre Geim became interested in graphene and challenged a Ph.D. student to polish a hunk of graphite to as few layers as possible. The student was able to reach 1,000 layers, but could not hit Geim’s goal of 10 to 100 layers. Geim tried a different approach: tape. He applied it to graphite and peeled it away to create flakes of layered graphene. More tape peels created thinner and thinner layers until he had a piece of graphene 10 layers thick, Geim’s team worked at refining their technique and eventually produced a single layer of carbon atoms. They published their findings in “Science” in October 2004, Since those first flakes made with tape, graphene production has improved at a rapid pace. In 2009, researchers were able to create a film of graphene that measured 30 inches across, In 2010 Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov won the Nobel Prize in Physics “for groundbreaking experiments regarding the two-dimensional material graphene”.
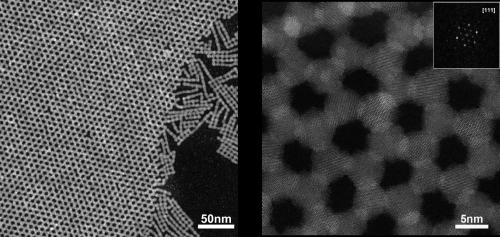
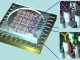
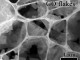
Graphene image by electronic microscope
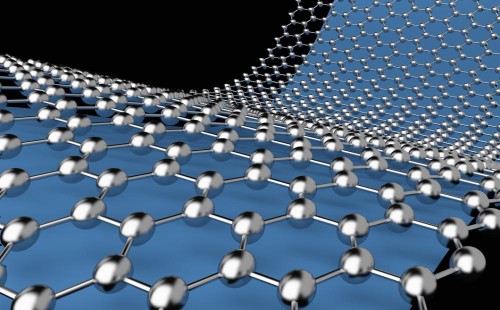
Graphene Structure:
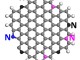
Graphene is a thin layer of pure carbon an allotrope of carbon in the form of a two-dimensional, tightly packed layer of carbon atoms that are bonded together in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice. In more complex terms, it is an allotrope of carbon in the structure of a plane of sp2 by Orbital hybridization bonded atoms with a molecule bond length of 0.142 nanometres, in 3D look Graphene consistent of Layers of graphene stacked on top of each other from graphite, with an interplanar spacing of 0.335 nanometres.
Graphene in atomic-scale, hexagonal lattice in which one atom forms each vertex. It is the basic structural element of other allotropes, including graphite, charcoal, carbon nanotubes, and fullerenes. It can also be considered as an indefinitely large aromatic molecule, the limiting case of the family of flat polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
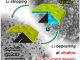
Graphene layer in atom scale
Graphene Properties :
Graphene has many extraordinary properties. It is about 200 times stronger than steel by weight, conducts heat and electricity with great efficiency and is nearly transparent. Researchers have identified the bipolar transistor effect, ballistic transport of charges and large quantum oscillations in the material.
and because of an amazing feature in Graphene as semiconductors can remove silicon uses and become Instead of it near future.
Graphene Uses :
Features of Graphene make it wonderful material and can use in many fields like electronics will create next generation of RAM, CPU, and all electronics parts because it have many advantages than silicon, in mechanic parts can make super strong parts and in safety can create bulletproof because Graphene the strongest material in the world!